Top 5 Advance Tech Used By Indian Armed Forces (2023)

The Need For Advance Technologies
India has always been in difficult scenarios when it comes to dealing with her neighbors. Even though India has preached and followed the mantra of :
Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam
(Sanskrit: वसुधैव कुटुम्बकम. from “vasudha”, the earth; “iva”, is ; and “kutumbakam”, family)
, the same demeanor hasn’t been reciprocated by all its neighbors. And in a world where India has found herself in situations where hostile forces have tried to harm her constantly , the efficiency of Indian armed forces is paramount.
For this very purpose, India has always been active in procuring the best equipment and technologies for the Indian armed forces. Now, it’s a proven fact that :
A sword is only as good as the man who wields it
And the very fact that one of Indian Air Force’s fighter pilot have been successful in bringing down a F-16 fighter jet (4th-generation) with MiG-21 Bison fighter jet (3rd-generation) demonstrates the capabilities of Indian armed forces. Such feats of valor have been a regular showing from all three branches of the Indian armed forces. From defending India in Kargil war(1999) to evacuating Indians during Kuwait Airlift (1990) , there are countless instances of Indian armed forces’ excellence. So, to elevate the proficiency of the armed forces , new and advance technologies and equipment are essential. This articles dives into some of the most advance technologies in Indian armed forces arsenal. Now, the list is based on factors like of being the absolute irreplaceable in their own class or grouping , unparalleled features and perfect fit for Indian subcontinent’s geography.
5. K9-Vajra (Army)
The K9-Vajra is self-propelled howitzer (SPH). A product of Larsen & Toubro (L&T) ,build in India, K9-Vajra ‘s underlying technology has been transferred from South Korean Hanwha Aerospace Defense based on its K9 Thunder. Being a short gun for firing shells on high trajectories at low velocities, the K9-Vajra is highly efficient in Indian-subcontinent conditions.
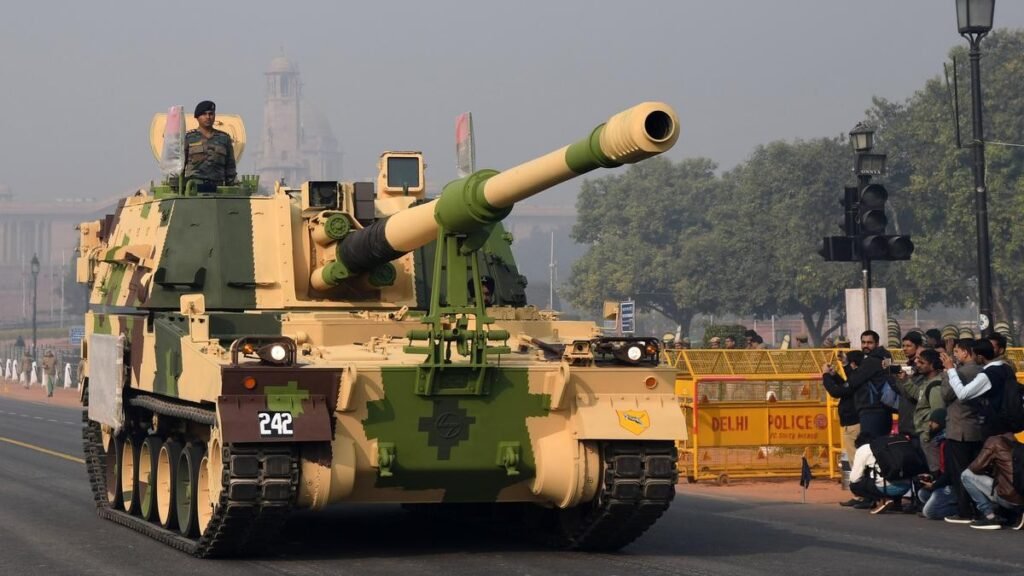

The gun weighs about 50 tonnes. With a 155 mm/52 calibre cannon, it can hit targets in ranges from 18-52 km, with 47kg bombs . K9-Vajra has a maximum range of 24,000 metres to 30,000 meters with high explosive ordnance and base bleed shells (Base bleed shells are bombs that have fire in their bottoms while being propelled through the air).
K9-Vajra’s powerful engine gives it a speed of 67 km/hours and requires a crew of five soldiers. It has characteristics of both a tank and a cannon with all-welded steel armour protection keeping it completely safe from enemy fire alongside the track that helps it to run fast in all kinds of fields.

Due to many capabilities of K9-Vajra, deployment along the LAC has been also done.
4. S-400(Air Force)

S-400 triumf missile system is a mobile and very long range surface-to-air missile(LR-SAM) defense system. the missile system is one of the most realiable defense mechanism with capabilities to destroy almost any kind of aerodynamic target including ballistic missiles. Developed by Almaz Central Design Bureau, the S-400 has been an upgrade from the older version of S-300 family. It has been fixed with multifunction radar for autonomous detection to counter any incoming air assault. The radar and detection parameters are so impressive as these help detect drones , unmanned aerial vehicles , aircrafts, guided missiles, cruise missiles and much more within a distance of 600km . Additionally , upto 300 such targets can be simultaneously detected by the missile system and upto 80 of the targets can be engaged simultaneously. S-400 is also capable to relay data to other defense systems like S-300 (its predecessor) , SA-12,SA-23.
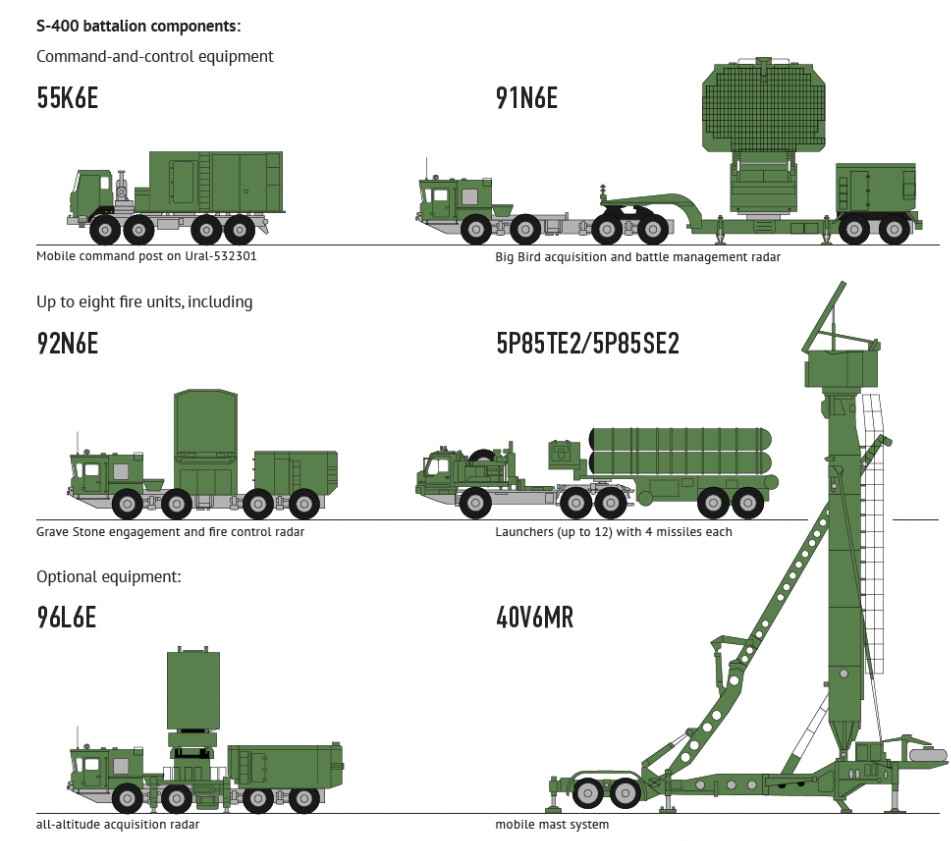
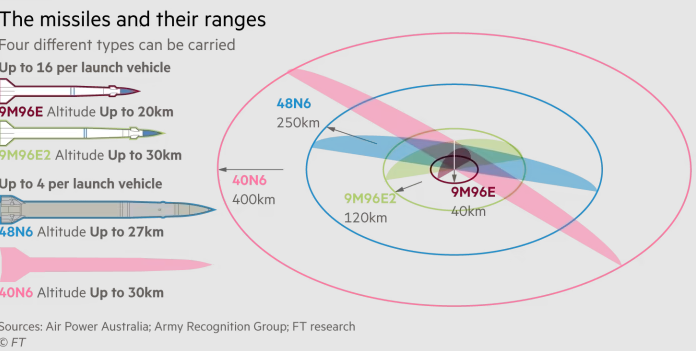
To fulfill the counter measures guided missiles are used by the defense system which can engage beyond visual range (BVR) bogeys upto a range 0f 400km and at an altitude of upto 30km for a layered defensive perimeter.
| Missile | Range |
| 48N6DM | Fully able to destroy airborne targets upto 250km and intercept ballistic missiles across a 60km radius. |
| 40N6 | Fully able to engage targets upto 400km. |
| 9M96E | Fully able to strike moving targets such as fighter aircraft with great accuracy upto 40km. |
| 9M96E2 | A medium-range air-to-air missile variant of the 9M96E, it is descended for direct impact, upto 102 km. |
For all these abilities India signed for a US$ 5.5 billion deal with Russia in 2018. The deal was to acquire 5 S-400 system squadron for the IAF. So far , three S-400 squadron have already been delivered . The first squadron, which was delivered by December 2021, has been placed and deployed near Pathankot ( northwest Punjab). The second squadron , which was delivered by April 2022, has been rolled out near the Siliguri Corridor (West Bengal) , The third squadron , which was delivered earlier this year, has been situated in western Rajasthan.
Also Read, How S400 Air Defence System Works?
3.INS Vikrant (Navy)
Also known as Indigenous Aircraft Carrier 1 (IAC-1), INS Vikrant has been designed by the Navy’s Warship Bureau and constructed by Cochin Shipyard in Kochi, Kerala . It is the 1st aircraft carrier to be indigenously built in India for the Indian Navy. The vessel got its name from its predecessor and India’s inaugural aircraft carrier, INS Vikrant (1961).

INS Vikrant got commissioned into the Indian Navy in September of 2022. Since then the vessel has undergone several phases of dense and intense operations. These operations included operations and maneuvers like the landing and take-off of the Light Combat Aircraft (Navy) and MiG-29K which marked the integration of fighter jets with the Indian naval warship. The aircraft carrier is about 262 meters long and 62 meters wide equipped with around 2,200 compartments, designed for a crew of about 1,600 strong. The aircraft carrier is powered by 2 gas turbine engines and 4 general electric engines.
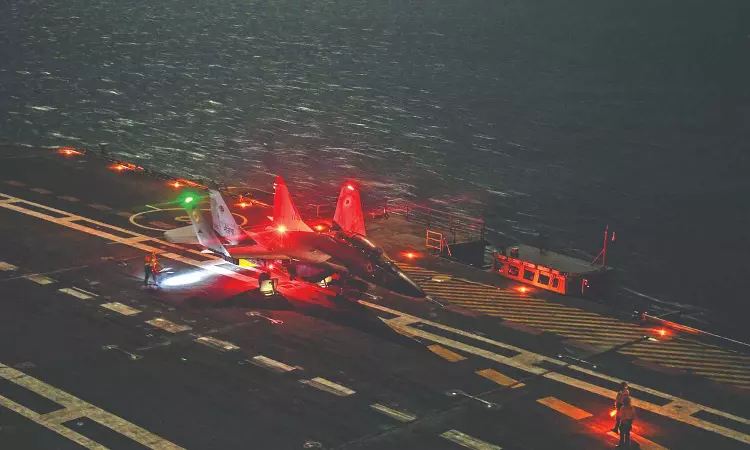

The ship can house an air wing consisting of about 30 aircrafts. These can consists of helicopters such as Kamov-31, MH-60R and Advanced Light Helicopters (ALH). They are launched from its ski-ramp style deck and the ship is also equipped with defensive systems including surface-to-air missiles.
At the moment, INS Vikrant has been deployed at Katuppali naval base located near Chennai. After the Rambilli Naval base is ready, located near Vizag in Andhra Pradesh, it will be shifted there. The base is also called “Varsha”. The underlying purpose of the Varsha naval base is to de-congest the Vizag port that is being used for both military and civilian purposes.
2.LCA Tejas (Air force)
LCA Tejas is a 4.5 generation fighter jet, designed to be a multi-role aircraft. It is capable of taking up offensive air support, close combat as well as ground attack role.

It is dimensionally the smallest and coupled with extensive use of composite structure also the lightest aircraft in its class. Designed with compound tail-less delta LCA capacity to carry wider range of weapons like Bombs, Missiles is better and efficient. With an In Flight Refueling (IFR) Probe the range is enhanced during mission. LCA is fully controlled via redundant quadruplex digital fly-by-wire flight control system. It comes with 9 hard points. Therefore, capable to fire variety of weapons like Long Range BVR and WVR missiles and much more with absolute precision and accuracy.
Tejas is capable of carrying 8-9 tonnes of load. Therefore, it can fly with as many weapons and missiles as a Sukhoi, which weighs way more than LCA. But its biggest advantage is its speed being a lightweight fighter jet, which is about the speed of light (Mach 1.6-1.8).
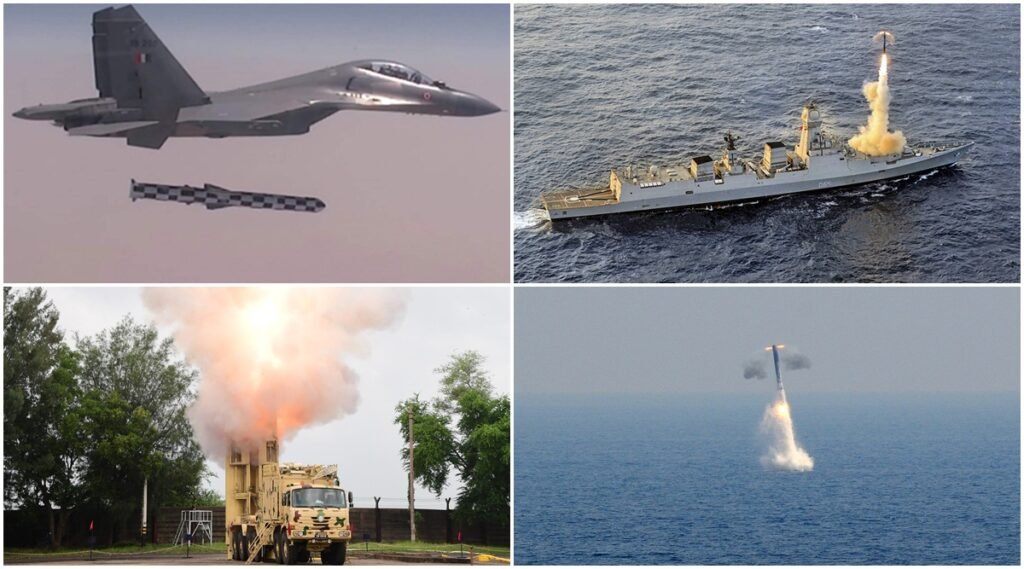
1.Brahmos (Army , Air force , Navy)
The BRAHMOS missile is a type of supersonic cruise missile that can be launched from various platforms like submarines, ships, fighter plane, or batteries on land. It is currently the fastest supersonic missile in the world.

BRAHMOS has been jointly developed by DRDO(India) and NPOM(Russia). The BRAHMOS , derives its name from the Brahmaputra (India) and Moskva rivers (Russia).The two entities ( Defense Ministry’s Defense Research and Development Organization and Russia’s Mashinostroyeniye Company) formed Brahmos Aerospace, that develops and manufactures the BRAHMOS PJ-10.
The BRAHMOS is distinguished by its reported supersonic speed of between Mach 2.0-2.8, depending on the cruising altitude used. While difficult to intercept, this speed is critical for a tremendous strike power. BRAHMOS is consists of stealth technology making it less visible to radar and other detection methods. Also it has 2 advance technologies of navigation system; inertial navigation system (INS) for ship targets and INS/Global Positioning System against for targets. Critical terminal guidance is possible due to an active/passive radar system onboard.

| Version | Length (in meters) | Body diameter (in meters) | Payload (in Kgs) | Range (in Km) | Speed (in Mach) |
| Ground | 8.2-8.4 | 0.67 | 200-300 | 290 | 2.8 – 3.0 |
| Air | 8.0 | 0.67 | 200 | 290 | 2.8 – 3.0 |
| Ship | 8.2-8.4 | 0.67 | 200-300 | 290 | 2.8 – 3.0 |
| Submarine | 8.2 | 0.67 | 200 | 290 | 2.8 – 3.0 |
The BRAHMOS carries either a 200 or 300 kg high explosive semi-armor-piercing warhead or a 250 kg submunitions warhead.
All the above mentioned are not the only advance technologies in Indian armed forces arsenal. There are many new and advance technologies that are being currently developed or are in production or are in trial phases. And in order to provide sturdy backing to the Indian armed forces these technologies are critical. As the world is rapidly evolving, the advance technologies are required to keep Indian armed forces as strong as possible to their true potential.




